Table of Contents
As a nurse, understanding the materials in surgical instruments is crucial for ensuring their effective use and maintenance. These materials determine the durability, safety, and performance of the instruments we rely on during surgeries. In this post, we’ll explore the common materials in surgical instruments and their specific applications.
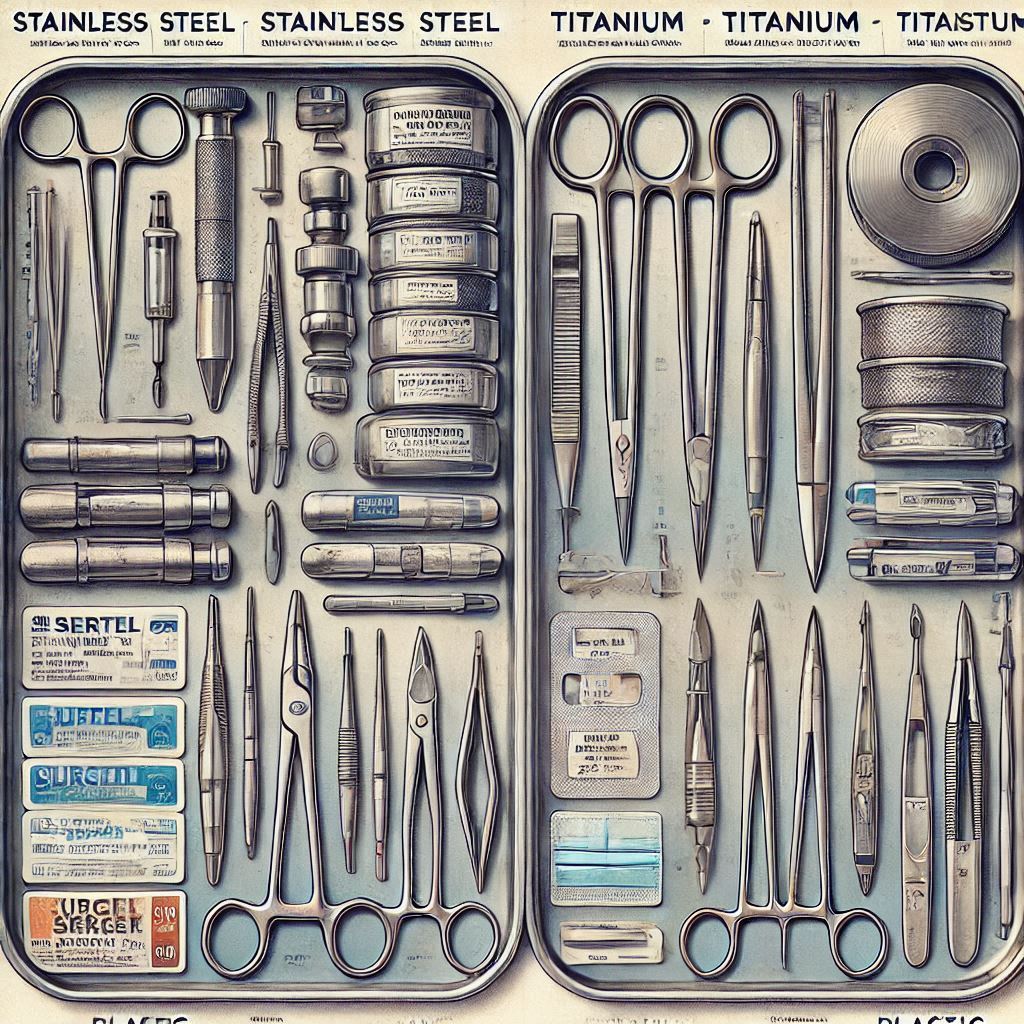
Stainless Steel as a Materials in Surgical Instruments
Stainless steel is one of the most common materials in surgical instruments. It’s known for its strength, durability, and resistance to rust and corrosion. This makes it ideal for instruments that need to be sterilized frequently.
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel is resistant to rust, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of surgical instruments.
- Strength and Durability: It can withstand the physical demands of surgical procedures.
- Biocompatibility: Stainless steel is safe for use in the body and does not cause adverse reactions.
Example Instruments:
- Scalpels: Used for making precise cuts. Stainless steel scalpels are preferred for their durability and ability to maintain a sharp edge.
- Forceps: Used for grasping and holding tissues. Stainless steel forceps are essential for handling tissues without causing damage.
- Needle Holders: Used to hold needles securely during suturing. Stainless steel needle holders provide a secure grip and are easy to sterilize.
Stainless steel is highly valued in surgical instruments due to its reliability and long-lasting performance. It’s versatile and used in various instruments, from simple scalpels to complex retractors.
Stainless steel instruments are essential in surgical procedures because of their strength and versatility. Their resistance to rust and corrosion ensures they can be used repeatedly without compromising their integrity, making them a staple in surgical settings. The biocompatibility of stainless steel also means that these instruments do not cause adverse reactions when used in the body, ensuring patient safety.
Titanium as a Materials in Surgical Instruments
Titanium is another essential material in surgical instruments. It’s lightweight, strong, and highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various medical tools.
- Lightweight: Reduces hand fatigue during long surgeries.
- High Strength: Ensures durability and reliability.
- Corrosion Resistance: Does not rust, even after repeated sterilizations.
- Biocompatibility: Minimizes the risk of allergic reactions.
Example Instruments:
- Hemostats: Clamps used to control bleeding. Titanium hemostats are lightweight and reduce strain on the surgeon’s hands.
- Surgical Scissors: Used for cutting tissues and sutures. Titanium scissors offer precise cutting with less hand fatigue.
- Bone Plates and Screws: Used in orthopedic surgeries. Titanium bone plates and screws are strong, lightweight, and compatible with the body.
Titanium’s properties make it ideal for high-precision instruments that require both strength and lightness. It’s particularly useful in orthopedic and neurosurgical procedures.
Titanium’s lightweight nature is a significant advantage in lengthy surgical procedures, where hand fatigue can be a concern. Its high strength ensures that instruments made from titanium are durable and reliable, providing consistent performance over time. The corrosion resistance of titanium means that these instruments can withstand repeated sterilizations without rusting, maintaining their integrity and safety. Additionally, the biocompatibility of titanium minimizes the risk of allergic reactions, making it a suitable material for implants and other surgical tools used in the body.
Carbon Steel as a Materials in Surgical Instruments
Carbon steel is known for its sharpness and hardness. It’s one of the best materials in surgical instruments that require extremely sharp edges.
- Sharpness: Carbon steel can be honed to extremely sharp edges, perfect for making clean cuts.
- Hardness: Maintains sharpness over time.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable, making it suitable for single-use instruments.
Example Instruments:
- Surgical Knives (Scalpels): Sharp blades for precise cutting. Carbon steel scalpels provide the sharpness needed for delicate procedures.
- Osteotomes: Chisels used for cutting or preparing bone. Carbon steel osteotomes maintain their sharpness and effectiveness over multiple uses.
Carbon steel’s sharpness and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for instruments that need to stay razor-sharp. However, it requires careful maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion.
Carbon steel’s ability to maintain a sharp edge makes it ideal for instruments that require precision and cleanliness in cuts, such as surgical knives and osteotomes. The hardness of carbon steel ensures that these instruments remain sharp over time, providing reliable performance in various surgical procedures. The cost-effectiveness of carbon steel also makes it a practical choice for single-use instruments, reducing overall costs while maintaining high-quality performance. However, the need for careful maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion is a consideration, highlighting the importance of proper care and storage for these instruments.
Tungsten Carbide as a Materials in Surgical Instruments
Tungsten carbide is often used for the cutting edges or tips of instruments. It’s super hard and stays sharp for a long time.
- Extreme Hardness: Keeps cutting edges sharp for longer periods.
- Wear Resistance: Suitable for frequent use and sterilization.
- Precision: Provides precise cutting and gripping capabilities.
Example Instruments:
- Needle Holders: The inserts help with a better grip and longer durability. Tungsten carbide needle holders offer superior control and precision.
- Scissors: Cutting edges made of tungsten carbide stay sharp longer. These scissors are used in procedures requiring meticulous cutting.
Tungsten carbide’s hardness and wear resistance make it ideal for instruments that need to maintain their performance over many uses. It’s a key material in high-precision tools.
Tungsten carbide’s extreme hardness ensures that instruments made from this material stay sharp for extended periods, reducing the need for frequent replacements or sharpening. This makes tungsten carbide an excellent choice for high-precision tools that require consistent performance over time. The wear resistance of tungsten carbide also means that these instruments can withstand frequent use and sterilization without degrading, maintaining their effectiveness and reliability. The precision provided by tungsten carbide instruments is crucial in surgical procedures that demand meticulous cutting and gripping capabilities.
Ceramic as a Material in Surgical Instruments
Ceramic materials are increasingly used in surgical instruments. They have unique properties that make them valuable in the OR.
- Biocompatibility: Ceramics are very safe and don’t cause reactions in the body.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to rust and chemical reactions.
- Non-Magnetic: Suitable for use in magnetic environments, like MRI procedures.
Example Instruments:
- Ceramic Scalpels: Used for very precise and clean cuts. Ceramic scalpels provide ultra-sharp edges without the risk of corrosion.
- Surgical Implants: Such as dental and joint implants. Ceramic implants are biocompatible and long-lasting.
Ceramics offer a combination of safety, durability, and precision, making them a valuable addition to surgical instruments. Their non-magnetic properties are especially useful in specific medical environments.
The biocompatibility of ceramic materials ensures that they do not cause adverse reactions in the body, making them suitable for implants and other surgical tools used internally. The corrosion resistance of ceramics means that these instruments are resistant to rust and chemical reactions, maintaining their integrity and performance over time. Additionally, the non-magnetic properties of ceramics make them ideal for use in magnetic environments, such as MRI procedures, where other materials might interfere with the imaging process. The precision and cleanliness provided by ceramic scalpels are also significant advantages in surgical settings, ensuring accurate and safe procedures.
Detailed Use Cases and Benefits
Understanding the specific applications of these materials in surgical instruments helps us appreciate their importance:
- Stainless Steel Scalpels: Used in a wide range of surgeries for making initial incisions. Their durability ensures that they remain sharp throughout the procedure.
- Titanium Hemostats: Essential in cardiovascular surgeries for controlling bleeding quickly. Their lightweight nature reduces hand strain during lengthy procedures.
- Carbon Steel Osteotomes: Used in orthopedic surgeries to shape bones. Their sharpness allows for precise bone cutting, critical for successful outcomes.
- Tungsten Carbide Needle Holders: Common in microsurgery where precision is paramount. The hardness of tungsten carbide ensures that the grip remains firm and stable.
- Ceramic Surgical Implants: Increasingly used in joint replacements due to their biocompatibility and longevity. Ceramic materials reduce the risk of rejection and wear over time.
By understanding these detailed use cases, healthcare professionals can appreciate the unique benefits and applications of each material in surgical instruments. This knowledge enables them to select the appropriate instruments for specific procedures, ensuring optimal performance and patient safety.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Choice of Materials in Surgical Instruments
Choosing the right materials in surgical instruments is crucial for their performance and safety. Each material—stainless steel, titanium, carbon steel, tungsten carbide, and ceramic—offers unique benefits for different surgical applications. By understanding these materials, we can better appreciate the design and function of the tools we use to save lives.
As a nurse, knowing the properties of these materials helps you understand why certain instruments are used in specific procedures. It also enhances your ability to care for and maintain these tools, ensuring they remain effective and safe for patient use.
Stay Ahead in Your Studies!
Understanding the materials in surgical instruments is essential for any aspiring nurse or medical professional. Dive deeper into this topic by exploring more resources, discussing with your peers, and even experimenting with different instruments during your practical sessions.
Ready to take the next step? Share this guide with your classmates and start a study group to discuss these materials further. Don’t forget to check out these valuable resources:
Internal Links:
External Links:
- World Health Organization – Surgical Care: Information on global surgical care and best practices.
- National Institutes of Health – Sterilization and Disinfection: Detailed information on sterilization methods in healthcare.
We’d love to stay in touch and keep you updated with the latest insights and resources!
Join our Email List Today!
- Stay informed with exclusive content and updates.
- Receive expert tips and valuable resources directly in your inbox.
- Be the first to know about new articles, events, and more!
Fill out the form to subscribe now and be part of our growing community!
Let’s keep the learning and excitement going!
Join the conversation: What material do you find most fascinating, and why? Leave a comment below or connect with us on our social media channels. Let’s learn and grow together!