This Asthma Nursing Care Plan serves as a sample and should be customized based on the individual needs of the patient.
Asthma management requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to address the complex needs of each individual.
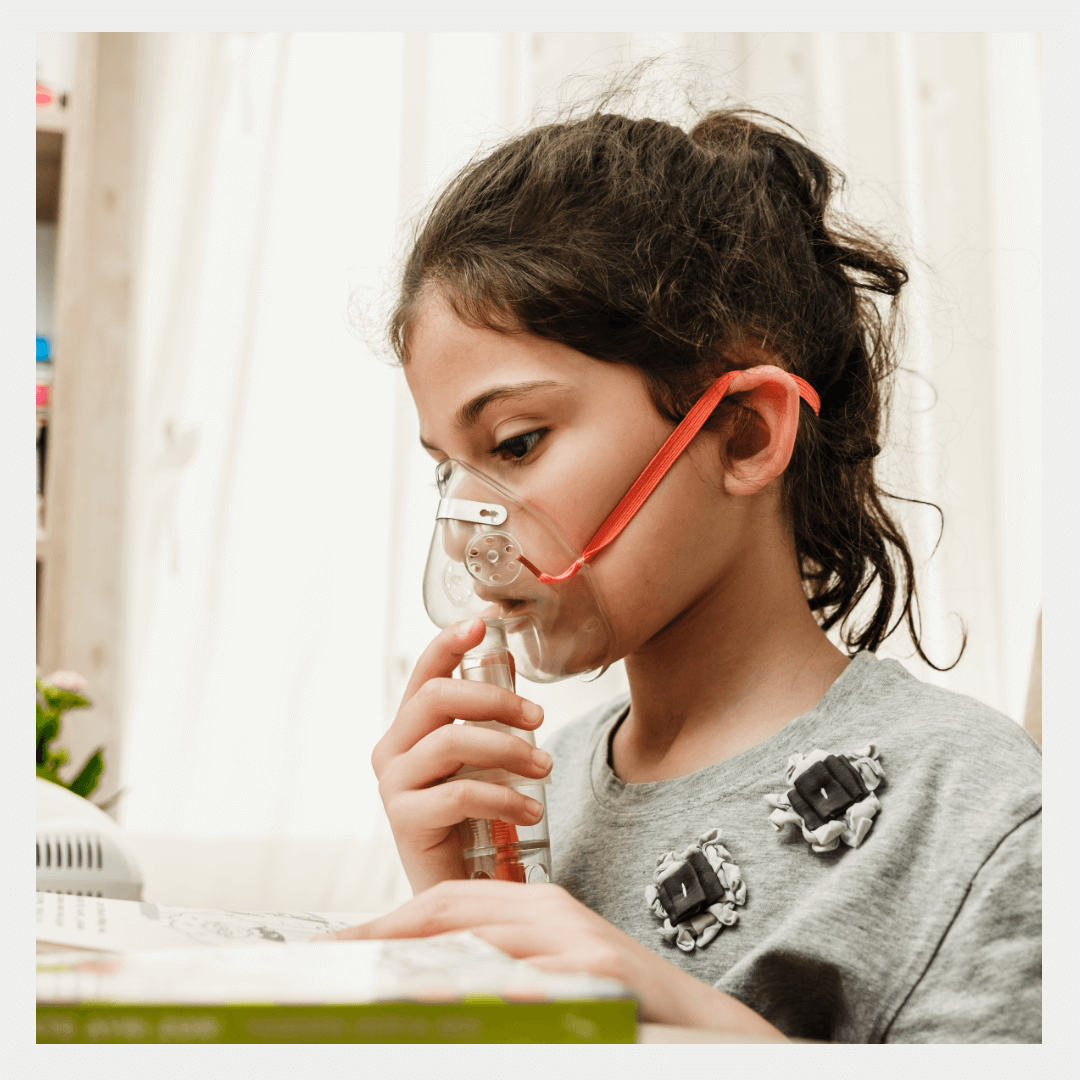
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest.
It is usually triggered by exposure to certain substances or environmental factors, such as allergens, pollutants, cold air, or exercise
Asthma Nursing Care Plan
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest.
It is usually triggered by exposure to certain substances or environmental factors, such as allergens, pollutants, cold air, or exercise.
Asthma symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary over time.
Management typically involves medications to control inflammation and bronchodilators to alleviate symptoms, along with lifestyle modifications and avoidance of triggers.
GOAL
- The patient will reduce asthma symptoms and improve lung function through medication adherence and avoidance of triggers.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
INDEPENDENT
1.)Monitor respiratory status frequently, including oxygen saturation and lung sounds.
- Rationale: Nurses can independently perform respiratory assessments to detect changes in the patient’s condition and initiate appropriate interventions
2.)Educate the patient on proper inhaler technique.
- Rationale: Nurses can independently provide education to ensure patients understand how to use inhalers correctly, promoting effective medication delivery.
3.)Teach the patient breathing exercises, such as pursed-lip breathing or diaphragmatic breathing.
- Rationale: Nurses can independently teach breathing exercises to help patients improve respiratory function and manage dyspnea.
4.)Provide education on asthma triggers and avoidance strategies.
- Rationale: Nurses can independently educate patients on identifying and avoiding asthma triggers to reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations.
DEPENDENT
1.)Administer bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) as prescribed.
- Rationale: Administration of medications requires a healthcare provider’s order, and nurses carry out this intervention based on the prescriber’s instructions.
2.)Encourage compliance with prescribed medications and follow-up appointments.
- Rationale: Nurses support medication adherence, but the prescription of medications and scheduling of follow-up appointments are typically determined by healthcare providers.
COLLABORATIVE
1.)Collaborate with other healthcare team members, such as respiratory therapists or allergists.
- Rationale: Collaboration with respiratory therapists and allergists allows for comprehensive asthma management, incorporating specialized expertise and resources to address the patient’s individual needs effectively.